


Gallery
View GalleryWhy Breast Sagging Occurs After Breastfeeding
All women at some point in their life will experience their breast start to sag. This is called ptosis and is a natural, inevitable process for the female body. The most notable sagging occurs with the process called breast involution (the process where the milk-making system inside the breast shrinks because it is not needed anymore). But breasts can have drooping start to occur in some aspect at any age.
A woman’s breasts are composed of fibrous tissue and fatty tissue. Both of these types of tissues will be affected by the weight of gravity. This downward pull of gravity will pull the breasts down and cause the breast ligaments will loosen. This, in turn, will put tension on the overlying breast skin causing stretching. The amount of sagging depends on the elasticity of your skin and ligaments.
A woman’s own elasticity differs from person to person and is determined by genetic makeup, life experiences (diet, smoking habits, pregnancies), as well as the normal aging processes. There is the obvious condition that large breasts have more mass and will tend sag and/or stretch more easily.
During pregnancy, the breast tissue grows in size due to the large amounts of estrogen that is produced by a mother’s body. This process prepares a mother’s breasts for lactation and allows for breastfeeding. The overall process can result in a condition known as breast hypertrophy – the disproportionate growth of one or both breasts compared with the rest of the body.
Hormones are vital chemical substances in the human body that act as ”chemical messengers,” carrying information and instructions from one group of cells to another. Hormones influence almost every cell, organ, and function in the human body. They regulate human growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, assimilation of food, response to emergencies, and even moods. Estrogen is a type of female hormone and is uniquely responsible for the growth and development of female sexual characteristics and reproduction. Estrogen is produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands, and fat tissues. Estrogen circulates in the bloodstream of the female body and binds to estrogen receptors on cells in targeted tissues. This affects not only the breast and uterus but also the brain, liver, heart, bone and other tissues. Estrogen also controls the growth of the uterine lining during the first part of the menstrual cycle, causes changes to the breasts during adolescence & pregnancy, and regulates various other metabolic processes including cholesterol levels and bone growth.
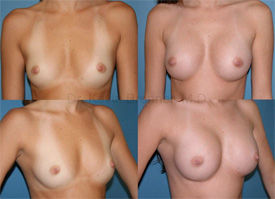
Breast involution usually happens after weaning from breastfeeding. What occurs is the tissues inside the breast shrink and the skin surrounding it doesn’t, causing the breast to look empty or deflated and therefore tends to sag. A woman’s body usually deposits fat back to the breast after weaning from breastfeeding so that breasts may rebound to their pre-pregnancy size, but this process can take months. However, many women after completing breastfeeding will actually lose volume, and their breasts become smaller than their pre-pregnancy breast size. This can lead to the mother feeling discontent and a low self-esteem with respect to their breast size and shape. Fortunately, these problems can be easily remedied with breast rejuvenation surgery: mastopexy, breast augmentation and/or augmentation-mastopexy.
Can I Breastfeed After Receiving Breast Implants?
The short and simple answer is: yes.
There are going to be changes to your breast that could affect your breastfeeding. The sensation to your nipples may change after a breast augmentation surgery. Some women will actually develop increased sensation and some will have decreased sensation. Since sensory response from the nipple helps stimulate milk production, there could be a reduction of milk in cases where sensation is impaired. However, almost all changes in sensation are temporary and therefore will return to normal.

For patients that only receive breast implants, without breast lift or reduction, the chance of having impaired milk production is very low. However, if your breasts were augmented because of underdeveloped breasts (breast hypoplasia) or tuberous breast deformity (constricted breast), you could possibly have trouble producing enough milk.
The Arrival Of The IDEAL IMPLANT®
After years of research and testing, as well as consulting many women and plastic surgeons, we have accomplished a design of a saline-filled breast implant, now known as the IDEAL IMPLANT®.
- Recently approved by the FDA
- Lowered edges, allowing it to contour better to the best wall
- Designed to combine the best of both saline and silicone implants
- The natural result of silicone with the safety of saline

